Feeling overwhelmed by Section 301 tariffs? You’re not alone! In simple terms, Section 301 tariffs are additional taxes placed on imported goods from specific countries (especially China) when the U.S. believes those countries are engaging in unfair trade practices. The most notable Section 301 tariffs in recent years have been those imposed on Chinese imports, which began in 2018. Unsure if your Chinese imports are hit with Section 301 tariffs? Deepbeez Customs Duties Calculator will calculate tariffs of your products in just seconds.
Transform complex trade regulations into actionable insights that drive business success. Our platform translates regulatory jargon into clear guidance tailored to your specific industry and markets. We stand behind our technology with a team of experienced trade professionals who understand your challenges. Explore our solutions and gain the competitive edge that comes with compliance confidence.
What Is Section 301 Tariffs Explained?
What is Section 301 tariffs China? Section 301 tariffs are extra taxes the U.S. government imposes on imports from countries it believes engage in unfair trade practices. Think of them as America’s way of saying, “Play fair or pay more!” If you’re not still familiar with the concepts of what are customs duties and tariffs, you’re probably in a trouble finding your way!
These tariffs lead to a substantial increase in the cost of imported goods. Here, as an importer, you will face an additional tax, which has averaged around 25% of the total value of goods. For instance, importing $10,000 worth of goods with a 25% Section 301 tariff would result in an extra $2,500 in tax!! How’s that sound? Now, the real question is that how can you avoid penalties and delays at customs by correct HTS code for shipments?
The Office of the United States Trade Representative (USTR) handles these investigations under the authority of the Trade Act of 1974. When they find a country isn’t following trade agreements or is harming U.S. commerce, they can hit back with these additional duties.
Don’t miss: What is HS Code?
Four Waves of Tariffs on Chinese Imports
The tariffs rolled out in four major lists:
| List | Implementation Date | Value of Imports | Initial Tariff Rate | Current/Final Rate | Product Focus |
| List 1 | July 6, 2018 | $34 billion | 25% | 25% | Industrial tech, chemicals, machinery, electronics |
| List 2 | August 23, 2018 | $16 billion | 25% | 25% | Additional industrial materials and components |
| List 3 | September 23, 2018 | $200 billion | 10% | 25% (May 2019) | Nearly 8,000 products across multiple categories |
| List 4A | September 2019 | $300 billion | 10% | 7.5% (Feb 2020) | Consumer goods not covered in previous lists |
| List 4B | (Never implemented) | N/A | N/A | Suspended | Remaining subheadings |
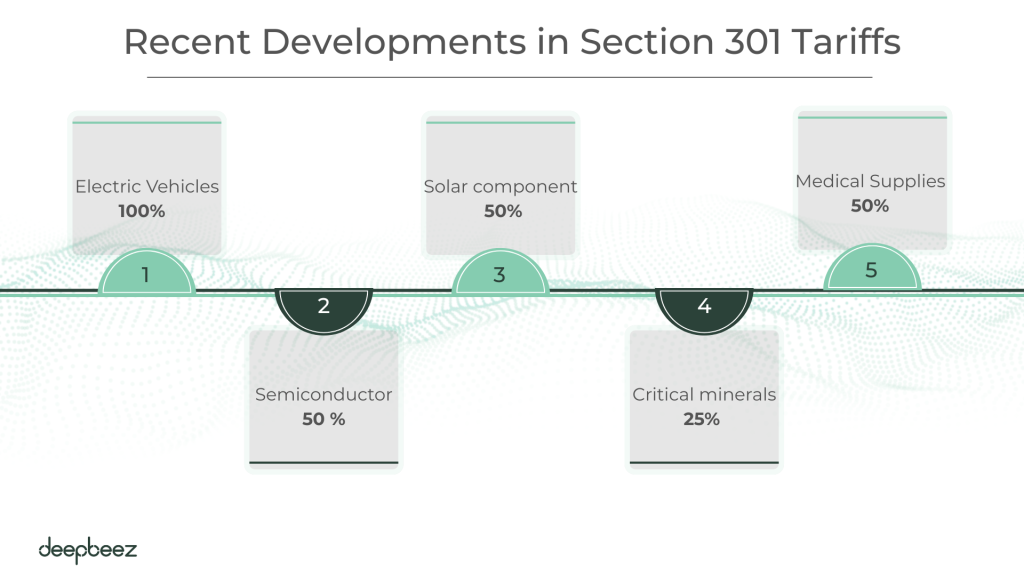
Recent Developments in Section 301 Tariffs in China Heat Up the Trade War
The Biden administration didn’t back down. After a four-year review in 2024, they actually increased many tariffs:
- Electric vehicles saw tariffs skyrocket to 100%
- Semiconductor tariffs jumped to 50%
- Solar component duties increased to 50%
- Critical minerals faced new 25% tariffs
- Medical supplies like face masks and syringes saw duties rise to 25-50%
In early 2025, the situation intensified further:
- The administration boosted the general tariff on Chinese products from 10% to 20%. Find out which Chinese products have increase tariffs.
- A separate executive order added another 20% duty on all Chinese imports
- Officials suspended the de minimis provision that previously allowed smaller shipments to avoid these tariffs
- The tariff timeline keeps evolving, with more increases scheduled for 2026 on items like lithium-ion batteries, natural graphite, and medical gloves.
