Are you feeling overwhelmed by regulatory requirements? Do silos in your organization create confusion about who handles what risks? You’re not alone. Many organizations struggle with these challenges, but a well-implemented GRC strategy can transform these headaches into competitive advantages.
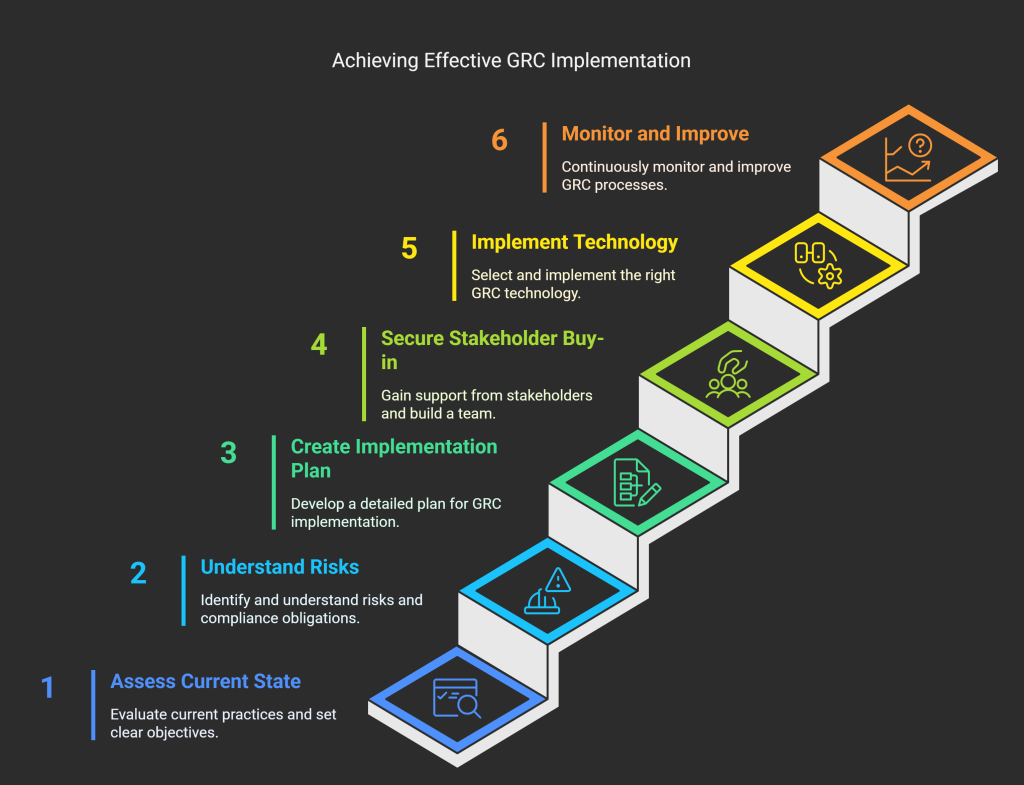
GRC implementation steps in a glance:
Step 1: Assess Your Current State and Define Clear Objectives
Step 2: Understand Your Risks and Compliance Obligations
Step 3: Create a Detailed GRC Implementation Plan
Step 4: Secure Stakeholder Buy-in and Build Your Team
Step 5: Select and Implement the Right GRC Technology
Step 6: Monitor, Evaluate, and Continuously Improve
What is GRC and Why Does It Matter?
GRC stands for Governance, Risk, and Compliance—three critical pillars that support your organization’s stability and integrity. When implemented correctly, GRC doesn’t just help you avoid problems—it creates value. Think of GRC as your organization’s immune system: it helps identify threats, establishes protocols to address them, and ensures your business stays healthy even when challenges arise.
Have you ever wondered how much time your team spends duplicating risk management efforts across departments? Or how many compliance gaps might exist simply because teams don’t communicate effectively? A proper GRC implementation addresses these issues head-on. In order to get better results from your GRC implementation, you need to be familiar with GRC best practices.
6 Key Steps to Successful GRC Implementation
In this guide, we’ll walk through every step of building a successful GRC program that works for your specific needs. No complex jargon—just practical, actionable advice that you can start using today.
Step 1: Assess Your Current State and Define Clear Objectives
Begin by taking an honest look at where you stand today. What GRC processes already exist in your organization? Which ones deliver value, and which ones create unnecessary work? You need to identify your most valuable assets and determine how they should be protected.
This assessment creates your foundation. By understanding your starting point, you’ll set realistic objectives that align with your business goals. Remember, effective GRC isn’t about checking boxes—it’s about creating systems that support your organization’s mission and protect what matters most.
Step 2: Understand Your Risks and Compliance Obligations
What keeps your leadership team up at night? Is it cybersecurity threats, operational vulnerabilities, or staying compliant with changing regulations? Your GRC program needs to address your specific risk landscape.
Conduct thorough risk assessments using both quantitative and qualitative methodologies. Map potential threats to your business operations and determine their potential impact. Simultaneously, identify all relevant regulations, standards, and internal controls your organization must manage—from well-known requirements to local obligations.
Do you know where your current compliance gaps are? Perform an internal compliance audit to compare your current posture with applicable regulations. This gap analysis will highlight exactly where you need to focus your efforts.
Step 3: Create a Detailed GRC Implementation Plan
A successful GRC program needs a roadmap. Your plan should outline progressive activities, specific processes, and realistic timelines for implementation. Don’t create the plan in isolation—involve key stakeholders from across your organization to ensure buy-in and practical insights.
Your implementation plan should clearly define:
- The scope of your GRC program
- Roles and responsibilities within the framework
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to measure success
- Impact on current workflows
- Communication channels
- Implementation metrics
- Strategies for handling identified risks
Are you wondering where to start with such a comprehensive plan? Consider focusing on one GRC component initially, then expanding based on early successes and lessons learned.
Step 4: Secure Stakeholder Buy-in and Build Your Team
Even the most perfectly designed GRC program will fail without proper stakeholder engagement. Start at the top—executive buy-in is non-negotiable. Demonstrate the financial impact of your GRC program to gain leadership support. Show how the program will protect revenue, reduce costs, and create efficiency.
Don’t forget about the departments most affected by your GRC initiatives. Involve them early in the process and gather their feedback. Their insights can help refine your approach and prevent implementation roadblocks later on.
Have you considered who will actually run your GRC program? Appoint a competent team with well-defined roles and ensure they have the support they need to succeed. Develop comprehensive training programs for all employees—everyone plays a role in your organization’s risk management and compliance efforts.
Step 5: Select and Implement the Right GRC Technology
In today’s digital world, the right technology can make or break your GRC program. Choose a GRC solution that aligns with your specific organizational needs. Consider factors like:
- User-friendliness
- Required capabilities (policy management, risk assessments, compliance monitoring)
- Workflow automation options
- Integration with existing systems
- Budget constraints
Remember that technology is a tool, not a solution on its own. The best GRC software still requires proper implementation and user adoption to deliver results. Integrate your chosen technology into your organization-wide processes and ensure everyone understands how to use it effectively.
Step 6: Monitor, Evaluate, and Continuously Improve
A successful GRC program is never “finished”—it evolves as your organization and risk landscape change. Implement monitoring mechanisms that enable real-time oversight of your program’s performance. Define clear metrics and indicators to track progress and identify areas for improvement.
How often should you review your GRC program? Establish a regular review period—whether quarterly, semi-annually, or annually—to evaluate effectiveness and incorporate learnings. Create a system for continuous improvement through scheduled audits and reviews, adjusting your approach based on emerging risks, regulatory changes, and evolving best practices.
Ask yourself: Is our GRC program becoming more efficient over time?
Are we seeing fewer incidents?
Are audit findings decreasing?
These questions help ensure your program delivers increasing value to your organization.
Common GRC Implementation Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Every GRC implementation faces obstacles. Being prepared for these challenges helps you navigate them successfully.
| Challenge | Description | Solution |
| Siloed Communication | Department-level communication lacks horizontal collaboration, creating blind spots in interconnected GRC tasks | Implement cross-functional teams and communication platforms; establish regular interdepartmental meetings focused on GRC issues |
| Lack of In-house Expertise | Insufficient skilled professionals in IT, security, and legal areas to develop and maintain an effective GRC program | Invest in training existing staff; consider bringing in external consultants; use technology to automate and simplify complex processes |
| Resource-Intensive Monitoring | Manual monitoring processes that consume considerable time and resources | Leverage technology for automated monitoring; prioritize high-risk areas; establish clear thresholds for escalation |
Don’t get discouraged if you encounter these challenges—they’re normal parts of the implementation process. With proper planning and the right approach, you can overcome them and build a stronger GRC program as a result.
Your GRC Implementation Checklist
Ready to get started? Here’s a practical checklist to guide your GRC implementation journey:
| Implementation Phase | Key Activities | Success Indicators |
| Assessment & Planning | • Evaluate current GRC practices• Identify risks and compliance obligations• Define objectives and scope• Develop implementation roadmap | • Clear understanding of current state• Documented risk profile• Defined success metrics• Detailed implementation plan |
| Preparation & Buy-in | • Secure executive sponsorship• Identify and engage key stakeholders• Appoint GRC team members• Select appropriate GRC technology | • Documented executive support• Cross-departmental engagement• Defined roles and responsibilities• Technology selection completed |
| Execution & Integration | • Roll out GRC processes• Implement technology solutions• Conduct training programs• Establish monitoring mechanisms | • Processes documented and followed• Technology successfully deployed• Completed training programs• Active monitoring in place |
Are there specific areas where your organization faces unique challenges? Adapt this checklist to address your particular needs and priorities. The most successful GRC implementations are tailored to fit the organization’s specific context.
Key Focus Areas for Different Industries
Different industries face unique GRC challenges. Finance organizations need robust controls around financial reporting and customer data protection. Healthcare providers must emphasize patient privacy and medical record security. Manufacturing companies often focus on operational safety and supply chain integrity.
What specific regulations impact your industry? How do your competitors address similar GRC challenges? Understanding your industry’s unique risk landscape helps you prioritize your GRC efforts effectively.
| Industry | Primary GRC Focus Areas | Key Regulations |
| Financial Services | • Fraud prevention• Anti-money laundering• Consumer protection | • Dodd-Frank• GDPR• PCI DSS |
| Healthcare | • Patient privacy• Medical record security• Clinical compliance | • HIPAA• HITECH• Various FDA regulations |
| Manufacturing | • Operational safety• Supply chain integrity• Environmental compliance | • ISO standards• OSHA regulations• Environmental protection laws |
How does your organization’s GRC focus align with these industry patterns? Are there areas where you might need to adjust your approach to better address industry-specific risks?
Is Implementing GRC Useful for Your Business?
Implementing a successful GRC program takes time, effort, and commitment—but the rewards are substantial. An effective GRC framework strengthens governance, lowers risk, and ensures compliance while supporting your business objectives. Remember that GRC implementation isn’t a one-time project but an ongoing process of adaptation and improvement.
Have you started your GRC journey yet? Whether you’re just beginning or looking to enhance an existing program, the steps outlined in this guide provide a roadmap to success. Start where you are, focus on what matters most to your organization, and build incrementally. With each improvement, your GRC program will deliver greater value and protection.
What’s your next step? Perhaps it’s conducting that initial assessment, securing executive buy-in, or evaluating technology options. Whatever it is, take that step today—your organization’s future security and success depend on it.
Ready to transform how your organization approaches governance, risk, and compliance? Let’s get started!
FAQ
1- How do we ensure our GRC implementation remains cost-effective?
For your strategy to be more scalable, sustainable and cost-effective, focus on incorporating GRC throughout your organization seamlessly rather than soiling it in a specialized department. Regularly evaluate ROI, prioritize high-impact initiatives, and leverage technology for efficiency.
2- How do we balance GRC requirements with business performance?
GRC ensures organizations meet third-party requirements while still hitting high-performance goals. Focus on integrating GRC into business processes rather than treating it as a separate function, emphasize efficiency through automation, and prioritize efforts based on risk.
3- What’s the role of automation and AI in modern GRC implementation?
When implementing automation and AI technologies in GRC, conduct an ethics impact assessment to identify potential risks and biases, evaluate compliance requirements, establish governance measures including clear policies and accountability, and implement mechanisms for ongoing monitoring.
4- How do we address data privacy concerns within our GRC strategy?
Conduct a thorough review of data privacy policies and procedures, assess data handling practices for compliance with regulations, identify gaps or vulnerabilities in data privacy controls, and implement corrective actions including employee training and enhanced monitoring.
5- How do we handle a situation where a new regulatory requirement must be implemented?
Thoroughly study the new requirement to understand its scope, objectives, and specific compliance obligations. Then assess current processes, identify gaps, develop an implementation plan, train staff, and establish monitoring mechanisms.
7- Which GRC framework should we adopt?
There are specialized GRC frameworks tailored to address specific industry needs and regulatory requirements (such as HIPAA, PCI-DSS, GDPR) and general governance frameworks focusing on decision-making and risk management (like BS 13500, COSO, ISO 37000). Choose based on your industry and specific requirements.
8- How frequently should we update our GRC framework?
After an organization defines a GRC framework, there is a need to constantly update and maintain it. Mitigating risk and staying compliant is an ongoing task that demands effort from all stakeholders. At minimum, review annually and whenever significant regulatory or business changes occur.
9- How do we handle cloud-specific GRC challenges?
Organizations are readily adopting cloud computing, resulting in major changes to organizational structures, networks, attack surfaces, and access control systems. GRC must adapt to this new paradigm. Implement cloud-specific governance policies, risk assessments, and compliance monitoring.
10- How do we integrate GRC with existing business processes?
Map your current business processes, identify touchpoints for GRC integration, and modify workflows to incorporate governance, risk, and compliance activities. With GRC eliminating the siloed mentality at work, more hands will collaborate toward goals aligned with the company’s vision.
11- Should we build our own GRC solution or buy a commercial platform?
This depends on your specific needs and resources. Building allows for customization but requires significant expertise and maintenance. Commercial platforms offer faster implementation and ongoing updates but may not perfectly fit your requirements. Most organizations find a hybrid approach works best.
12- How do we handle the challenge of manual GRC processes?
Manual processes can cause wasted time and human error. A lack of automation can lead to inefficiencies and difficulty locating required documentation, while also limiting visibility into data monitoring and collection. Implement automation where possible and use integrated GRC software.
13- How does GRC implementation differ for small businesses versus large enterprises?
The GRC framework offers advantages for organizations of any size. However, it’s especially valuable for large enterprises implementing cross-organizational governance, risk, and compliance programs. Small businesses can start with simplified frameworks focusing on highest-risk areas and core compliance requirements.
14- What are the most common challenges in GRC implementation?
Common challenges include keeping up with changing regulatory requirements, data silos, lack of employee accountability, declining visibility in GRC management, and compromised data integrity. LinkedIn Additionally, organizational resistance to change often impedes implementation.
15- How do I start building a GRC framework from scratch?
Start by clarifying why you need GRC and what objectives you want to achieve. Quora Then assess your current processes, identify gaps, secure leadership support, select appropriate tools, and develop an implementation roadmap with clear milestones.





